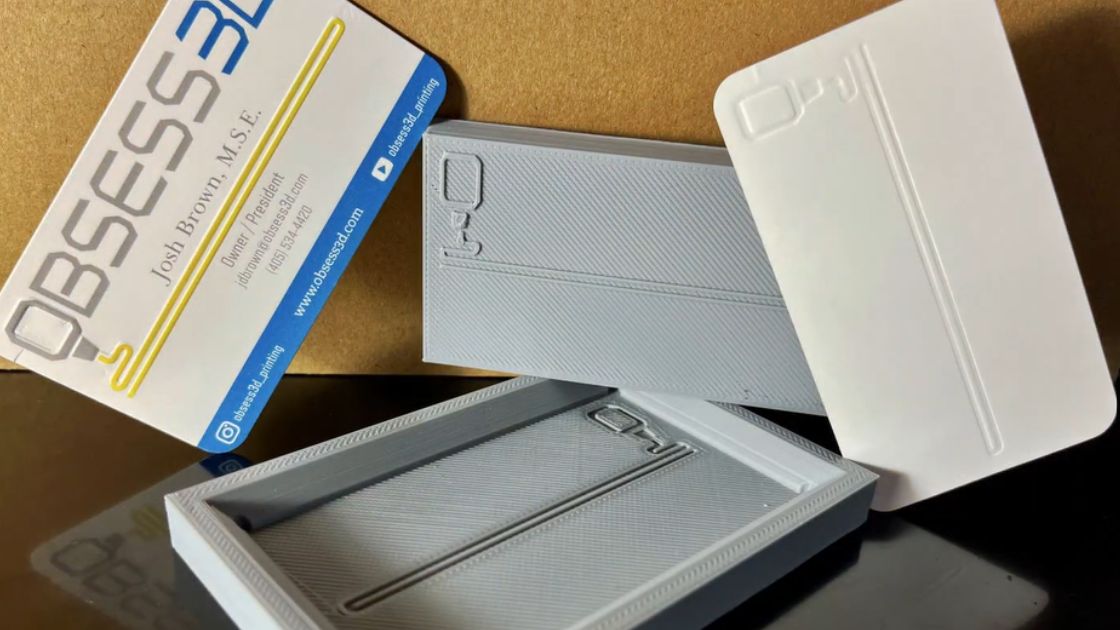
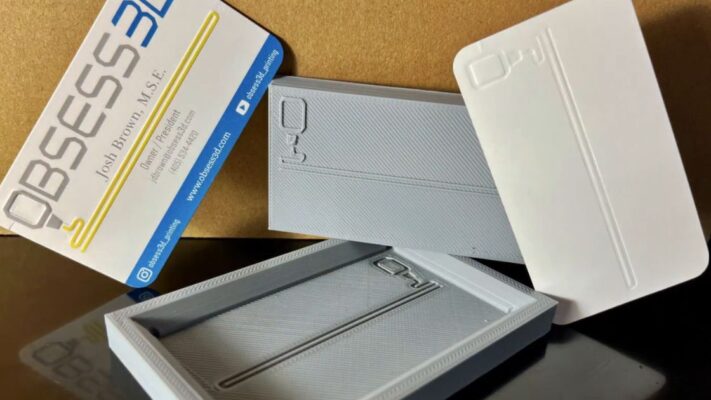
In the realm of creative design, innovation often leads to remarkable breakthroughs that transform the way we approach traditional techniques. One such innovation is the advent of 3D printed embossing plates, a technology that has revolutionized the process of adding intricate designs to various materials. In this article, we delve into the world of 3D printed embossing plates, exploring their uses, benefits, and the impact they have on design.
Contents
The Evolution of Embossing Plates
Traditionally, embossing plates were crafted through labor-intensive processes involving metal engraving or CNC machining. While effective, these methods were often costly, time-consuming, and limited in terms of design complexity. However, with the emergence of 3D printing technology, designers now have a more accessible and versatile tool at their disposal.
How 3D Printed Embossing Plates Work
3D printing technology has revolutionized various industries, including the realm of embossing and printing. Embossing plates, traditionally crafted through intricate machining processes, have now found a modern counterpart in 3D printing. Understanding how these innovative 3D printed embossing plates work unveils a world of possibilities for custom design and precision crafting.
Design Phase
The process initiates with meticulous design planning. Designers employ Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software to create digital models of the desired embossing patterns. These designs can range from intricate logos to finely detailed textures, depending on the intended application. Designers have the flexibility to experiment with various shapes, sizes, and depths to achieve the desired embossing effect.
Material Selection
Choosing the appropriate printing material is crucial to ensure the durability and effectiveness of the embossing plates. While a wide array of materials is compatible with 3D printing, certain characteristics such as hardness, flexibility, and heat resistance are paramount for embossing applications. Materials like photopolymer resins or thermoplastics, known for their strength and stability, are commonly preferred for crafting embossing plates.
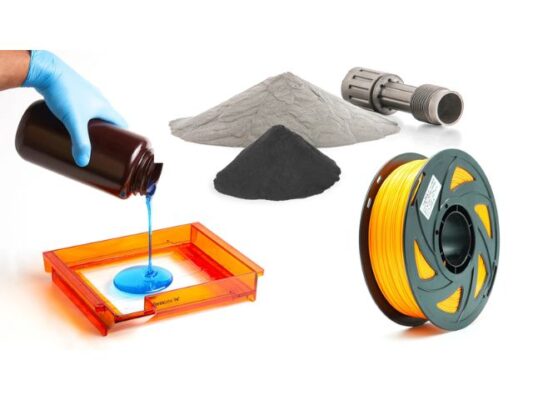

Printing Process
Once the design is finalized and the material selected, the 3D printing process begins. Utilizing additive manufacturing techniques, such as Stereolithography (SLA) or Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), the digital design is translated into physical embossing plates layer by layer. This additive approach enables precise control over the geometry and intricacies of the embossing patterns, ensuring high-fidelity replication of the digital design.

Post-Processing
After the printing is complete, post-processing steps are undertaken to refine the embossing plates further. This may involve curing the printed plates under UV light (in the case of photopolymer resins), removing support structures, and sanding or polishing the surfaces to achieve the desired finish. Post-processing is crucial for enhancing the durability, surface quality, and accuracy of the embossing plates.
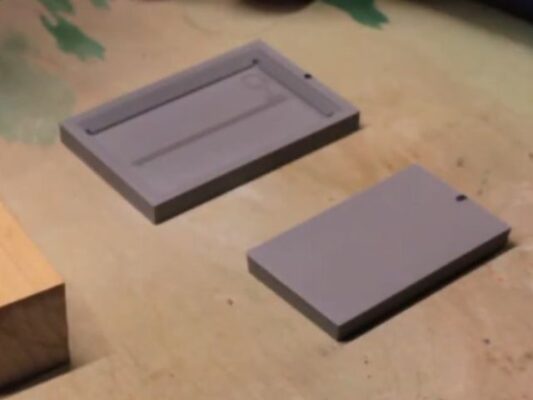

Integration with Printing Press
Once the embossing plates are fabricated, they are integrated into the printing press for actual embossing operations. The plates are securely mounted onto the press, aligning precisely with the substrate to be embossed. Depending on the printing technique employed (such as letterpress or flexography), the embossing plates exert pressure onto the substrate, creating raised patterns or designs that enhance the visual and tactile appeal of the printed material.
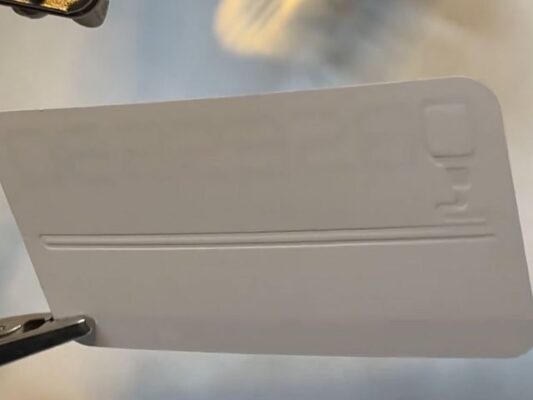

Applications of 3D Printed Embossing Plates
The versatility of 3D printed embossing plates opens up a myriad of creative possibilities across various industries:
- Packaging Design: Embossed packaging adds a touch of luxury and sophistication to products, enhancing brand identity and consumer appeal. 3D printed embossing plates allow for custom designs that elevate packaging aesthetics.
- Stationery and Invitations: From wedding invitations to business cards, embossed stationery exudes elegance and professionalism. 3D printed embossing plates enable designers to create bespoke designs that leave a lasting impression.
- Textile and Fashion: Embossed patterns can add texture and visual interest to fabrics and garments, creating unique tactile experiences. With 3D printed embossing plates, fashion designers can experiment with intricate designs and textures.
- Art and Crafts: Artists and craftsmen use embossing techniques to add dimension and detail to their creations. 3D printed embossing plates offer limitless design possibilities for art projects, scrapbooking, and DIY crafts.
The advent of 3D printed embossing plates represents a paradigm shift in creative design, empowering designers to explore new frontiers of innovation and expression. From packaging and stationery to textiles and art, the versatility and accessibility of 3D printed embossing plates unlock boundless opportunities for creativity and customization. As this technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more groundbreaking applications that push the boundaries of design possibilities.
Related Posts







